Cardiac tissue engineering- -a CS-GNP hydrogel
Electrically conductive gold nanoparticle-chitosan thermosensitive hydrogels for cardiac tissue engineering
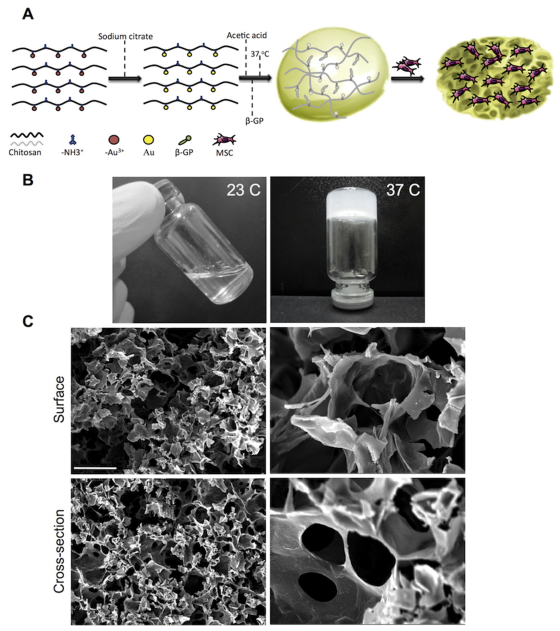
Injectable hydrogels similar to the mechanical and electrical properties of the myocardium are crucial for the promise of cardiac tissue engineering. We have developed a facile method that uses chitosan (CS) to generate thermosensitive electroconductive hydrogels of highly porous networks with interconnected pores. Gold nanoparticles (GNP) are uniformly dispersed throughout the CS matrix to provide electrical signals. The gelelling reaction and conductivity of the hydrogel were controlled by different concentrations of GNPs. The CS-GNP hydrogels were inoculated with mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) and were cultured for up to 14 days in the absence of electrical stimulation. The CS-GNP scaffold supports MSC viability, metabolism, migration, and proliferation, as well as the development of homogeneous cell constructs. Immunohistochemistry of early and mature cardiac markers revealed enhanced myocardial differentiation of MSC in the CS-GNP compared to the CS matrix alone. The results of this study suggest that incorporation of nanoscale conductive GNP into CS hydrogels enhances the properties of the myocardial construct. These constructs can be used for the regeneration of other electroactive tissues.
18915694570
Previous: Cardiac tissue enginee
Next: BK Engineering Bacteri


