Shanghai University Wang Yanli AFM: Organelle-specific anchored delivery system can be combined with chemotherapy-photothermal therapy to reverse tumor hypoxic microenvironment

The traditional targeted delivery system is mainly through pathological tissue delivery to achieve cell membrane targeting and release drugs in the cytoplasm. The delivery system can first reach the tumor tissue through the EPR effect, pass through the biological barrier, and gather in a specific organelle. However, only a small percentage of therapeutic drugs can successfully reach specific organelle targets. Therefore, direct delivery to subcellular organelles is the key to solving the high dose requirements and systemic toxicity due to lack of specificity. Compared with other organelles of eukaryotic cells, mitochondria with double membranes are the power source and weapon storehouse for cells to produce ATP. In addition to energy production, they are also involved in a variety of physiological activities, including reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, mitochondrial autophagy, metabolism, homeostasis, and apoptosis. In addition, mitochondria have also been shown to be susceptible to high heat. These characteristics make the mitochondrial-specific delivery of drugs a feasible strategy to improve efficacy.
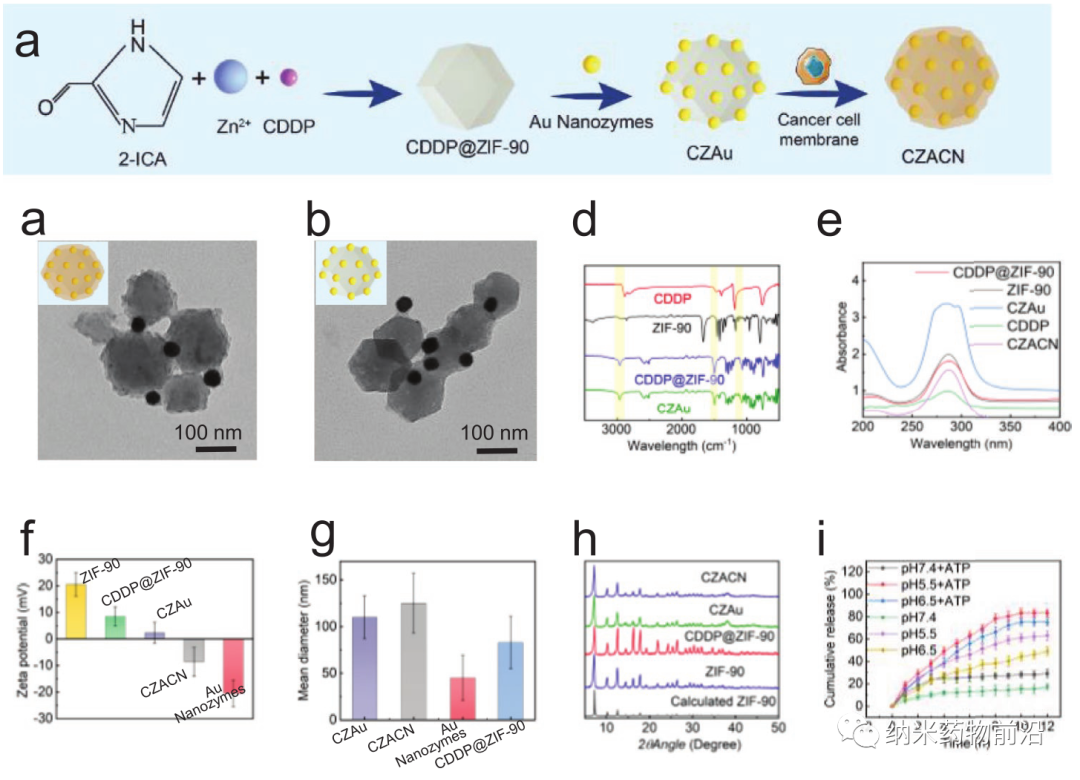
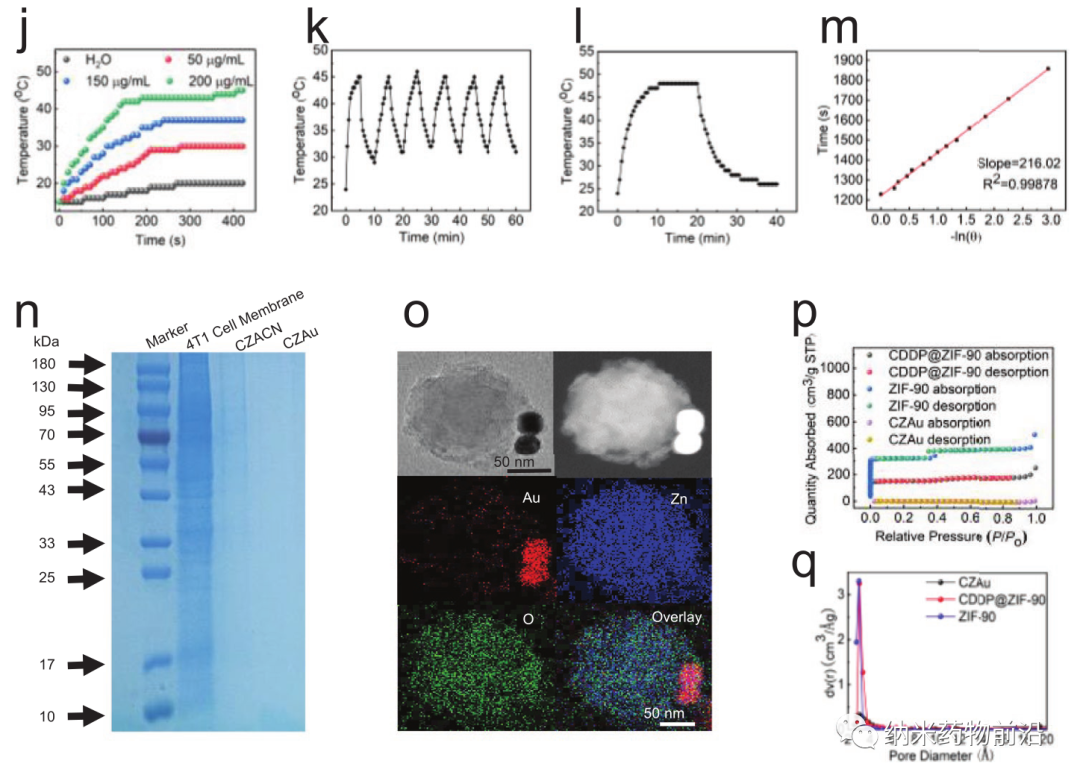
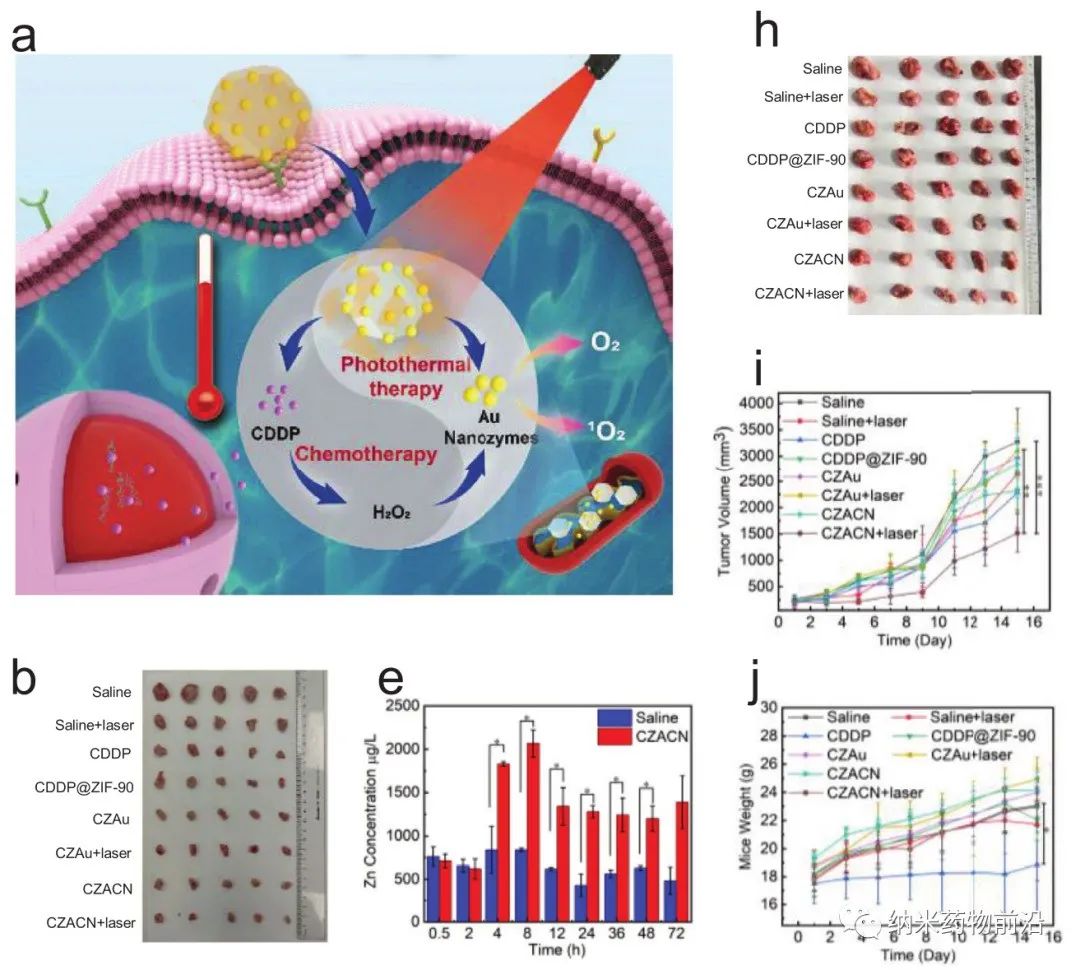
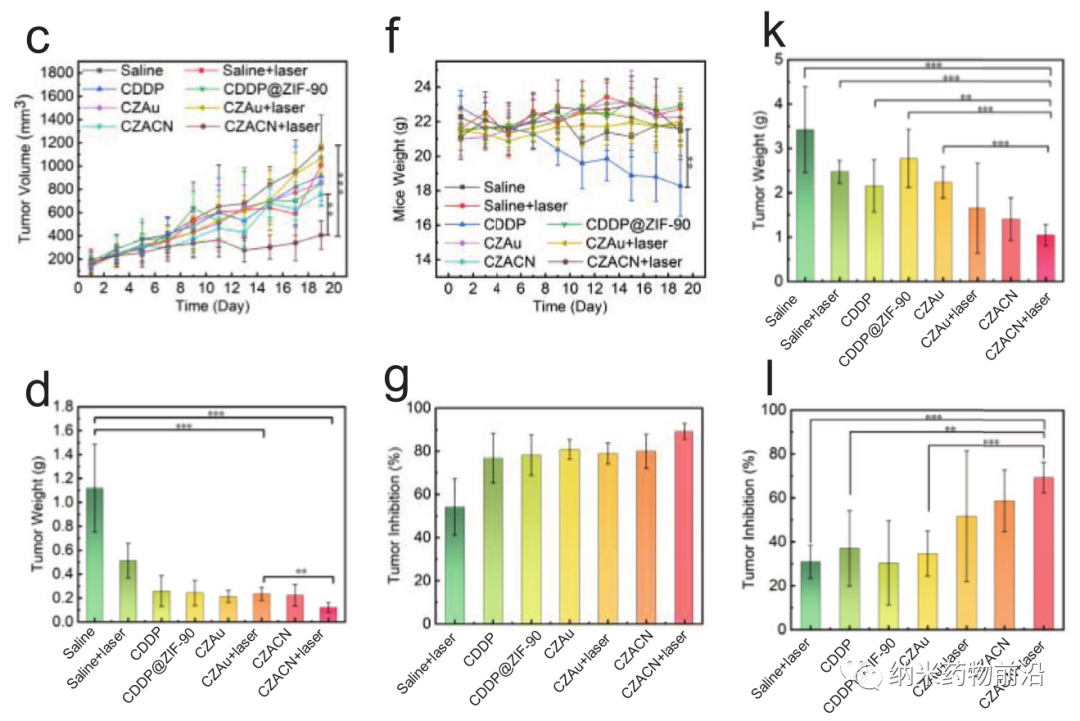
Here, Professor Wang Yanli of Shanghai University designed a mitochondrial targeting nanoplatform (CZACN). It consists of ZIF-90 for mitochondrial-specific delivery, cancer cell membranes for evading the immune system and targeting homologous cells, cisplatin (CDDP) for chemotherapy, and gold nanozymes for oxygen self-sufficiency and photothermal therapy composition. ZIF-90 is produced from other metal-organic frameworks. The structure of ZIF-90 is disintegrated due to the competitive coordination of ATP and zinc. Therefore, ZIF-90 is sensitive to high ATP dose environments. Since the ATP content in mitochondria is almost 25 times higher than that in the extracellular environment, zinc ions will be dissociated from ZIF-90, stimulate ROS production, and ultimately lead to cell apoptosis. ZIF-90 can be further wrapped by cancer cell membranes carrying cancer cell proteins and antigens, so that it can escape the immune system and target homologous tumor cells. CDDP is one of the typical platinum-based drugs. It interacts with nuclear DNA to form Pt-DNA adducts, cuts off gene replication and transcription, and ultimately leads to cell apoptosis and cell death. It can activate NADPH oxidase, produce O2•−, and produce H2O2 in cancer cells. However, because CDDP can be affected by hypoxic microenvironment of the tumor and inhibit the formation of Pt-DNA adducts, it can cause dose-limiting toxicity. In order to alleviate the tumor hypoxic microenvironment, the author coated gold nanozyme with ZIF-90. ZIF-90 has simulating enzyme catalytic properties, and its catalytic performance and stability are better than natural catalase. They can catalyze excess H2O2 to produce O2 and singlet oxygen under near-infrared light irradiation, alleviate tumor hypoxia, and enhance the toxicity to cancer cells. In addition, gold nanozymes have a good photothermal conversion effect under laser (650-1100 nm) irradiation. Experiments show that CZACNs have the characteristics of oxygen self-sufficiency, specific release of organelles and light-to-heat conversion. In addition, under near-infrared irradiation, the tumor growth inhibition rate can reach 89.2±3.70%, and the dose-limiting toxicity caused by CDDP is reduced. Mild hyperthermia at 52 ℃ in the near-infrared can also enhance its permeability and fluidity, ultimately increase its intracellular accumulation, and improve the effect of chemotherapy-photothermal therapy.
18915694570
Previous: MXene aerogel prepared


