Southwest Jiaotong University Zhou Shaobing/Guo Xing AM: Bacterial outer membrane vesicle-mediated tumor PD-L1 self-blocking enhances the effect of immunotherapy

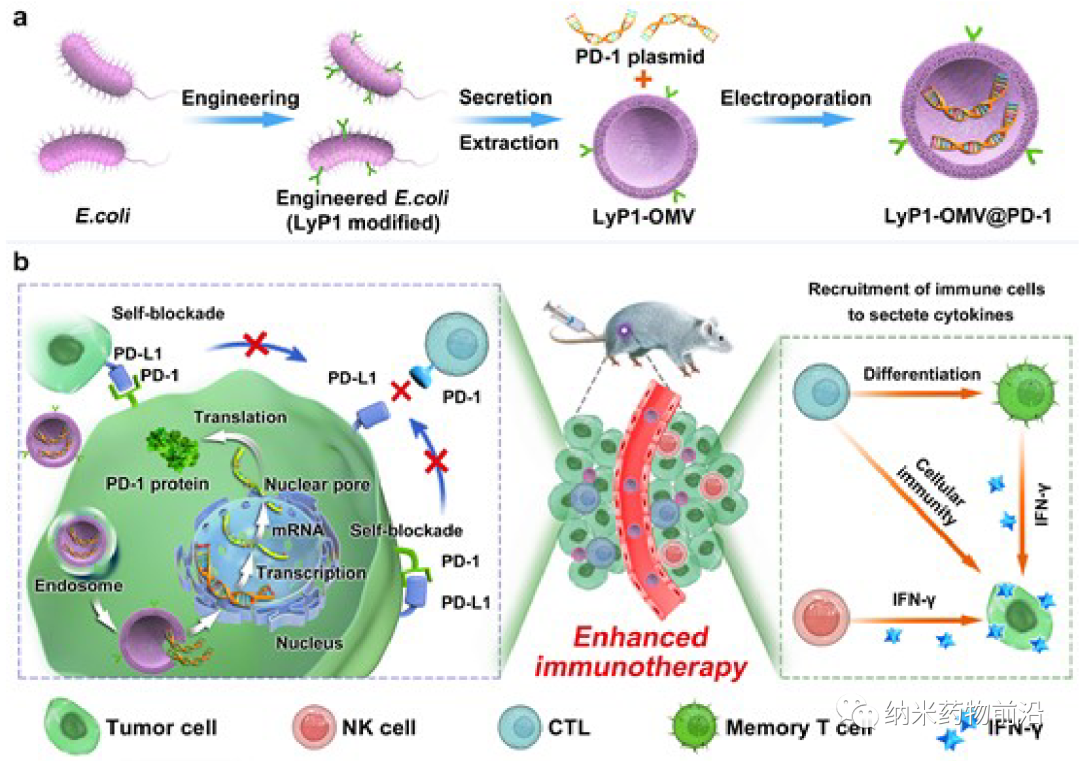
Here, Professor Shaobing Zhou and Professor Guo Xing of Southwest Jiaotong University developed a LyP1 polypeptide-modified bacterial outer membrane vesicle (LOMV) containing PD-1 plasmid, which realized the self-blocking of PD-L1 in tumor cells. Express the targeting polypeptide LyP1 in E. coli, extract LOMVs, and encapsulate the PD-1 plasmid to obtain LyP1-OMVs@PD-1 nanocarrier. After intravenous injection, these nanocarriers accumulate in tumor tissues through the targeting ability of OMV, and are internalized in tumor cells through LyP1, and then the PD-1 plasmid is sent to the nucleus, causing tumor cells to express PD-1. Self-expressed PD-1 binds to PD-L1 expressed by itself and neighboring tumor cells to achieve self-blocking, and CTL is reactivated to destroy tumor cells. At the same time, the outer membrane protein of LOMV can recruit cytotoxic lymphocytes and natural killer cells to tumor tissues, stimulate them to secrete IFN-γ, and improve the anti-tumor activity of PD-1/PD-L1 self-blocking therapy. In addition, OMVs differentiated CTL into central memory T cells, which produced long-term immunity. Experimental results show that, compared with non-targeted OMV, LyP1 has an effective ability to target tumors and accumulate in tumors. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles also attract CTL and NK cells to tumor tissues to achieve dual anti-tumor effects. This strategy has significantly improved the therapeutic effect of tumors and provides new ideas for the development of tumor immunotherapy nanomedicine.
Original link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/adma.202106307
18915694570
Previous: Nano Lett: Design a de


