[NML review] Multivariate detection technology helps the development of extracellular vesicle biomarkers
At present, there are no existing markers for many diseases or the existing markers (such as free protein in blood and urine) have low diagnostic accuracy. At the same time, extracellular vesicles carrying mother cell molecular marker fingerprints provide a treasure trove for the development of markers. It has shown great potential in the early diagnosis, course tracking, and treatment effect evaluation of cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases and other diseases.
Therefore, the development of exosomes detection technology to study the association of exosomes (membrane proteins, internal proteins, nucleic acids, metabolites, etc.) with diseases is of great significance to the development of diagnostic markers.
Compared with traditional one-element high-throughput ELISA, multiplex detection (multiplexing) can quickly detect multiple targets from one sample, which can greatly save valuable samples and time, and reduce the errors caused by multiple singleplexing. And variables. At the same time, a single marker often only reflects the characteristics of the limited dimensions of the disease. If several markers that are highly related to the disease can be screened, it will undoubtedly reflect the comprehensive dimensional characteristics of the disease more clearly. Based on this, the underlying technology of multivariate detection of exosomes can undoubtedly drive the development of extracellular vesicle markers.
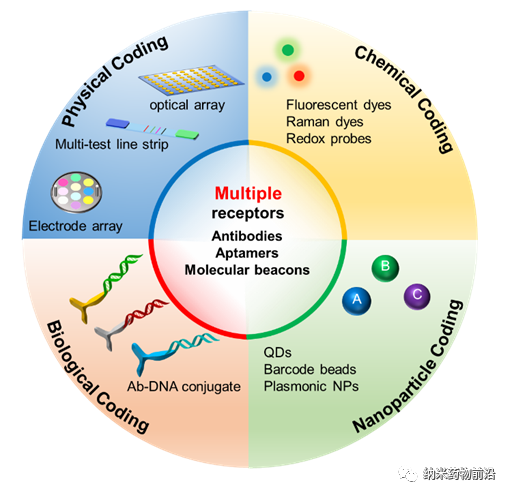
Dr. Cheng Jiang from the Department of Neuroscience and Department of Chemistry, University of Oxford, combined many years of experience in first-line clinical sample management and analysis and accumulated experience in the development of multiple high/low throughput sensor technology platforms. This article systematically explains the biological (such as DNA coding), physics (such as spatial position coding), chemistry (such as chemical dyes, electrochemical probe coding), and The coding strategy of nanoparticles (such as nanoparticle codes with optical properties or electrochemical activity) is used to realize the detection of multiple extracellular vesicle targets.
The article discusses how to use a variety of hardware technologies combined with big data and large clinical sample sequences to achieve high-throughput screening-high-throughput verification, screening the most relevant biomarkers of diseases from multiple omics dimensions, and constructing composite biomarkers and Finally, we have made an outlook towards Point-of-Care Testing.
Full text link: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00753-w
This information is sourced from the Internet for academic exchanges only. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately.
18915694570
Previous: ESM: The influence of


