AEM: Acid-free and alkali-free in-situ electrochemical synthesis of MXenes for aqueous zinc ion batteries

Research Background
In the past ten years, MXenes has developed into an important multifunctional two-dimensional material, which is widely used in the fields of liquid crystal, catalysis, sensors, nano-generators, seawater desalination and microwave shielding. At present, the conventional process for preparing MXenes energy storage devices includes the initial synthesis of MXenes and subsequent device assembly, which is a multi-step and complex process. More importantly, there are unavoidable safety risks in the synthesis of MXenes from acids or bases.
Introduction
Recently, the research group of Professor Chunyi Zhi from City University of Hong Kong published a research paper titled In Situ Electrochemical Synthesis of MXenes without Acid/Alkali Usage in/for an Aqueous Zinc Ion Battery in the well-known academic journal Advanced Energy Materials.
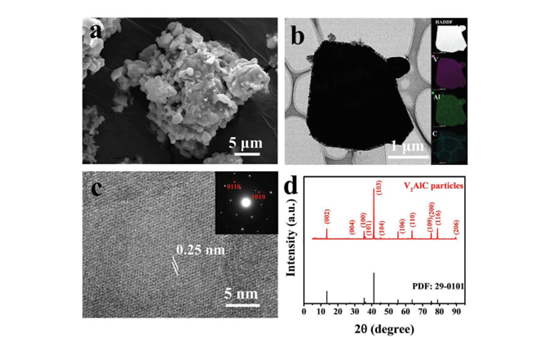
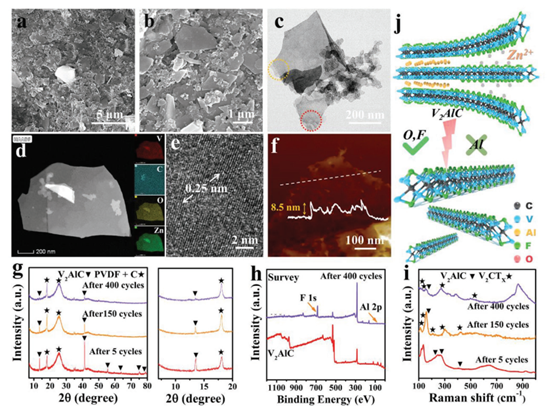
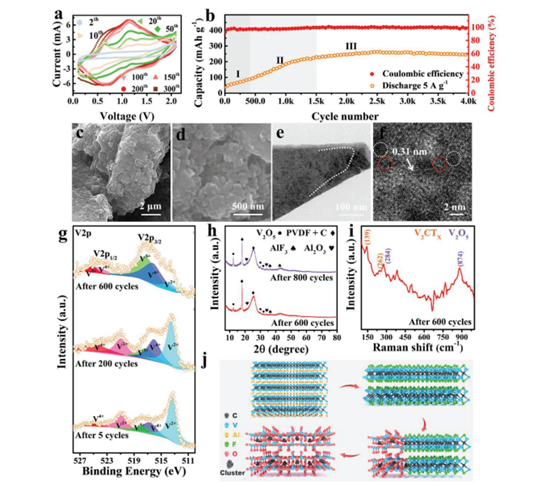
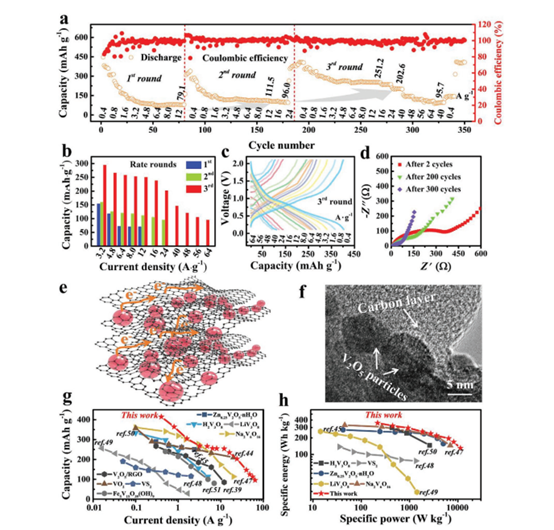
Figure 4. The electrochemical performance of the battery.
Summary of this article
DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202001791
This information is sourced from the Internet for academic exchanges only. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately.
18915694570
Previous: Nat Nanotechnol: Selec


