Liu Peifeng Adv Sci: New iron oxide nanoparticles inhibit tumor autophagy to treat liver cancer

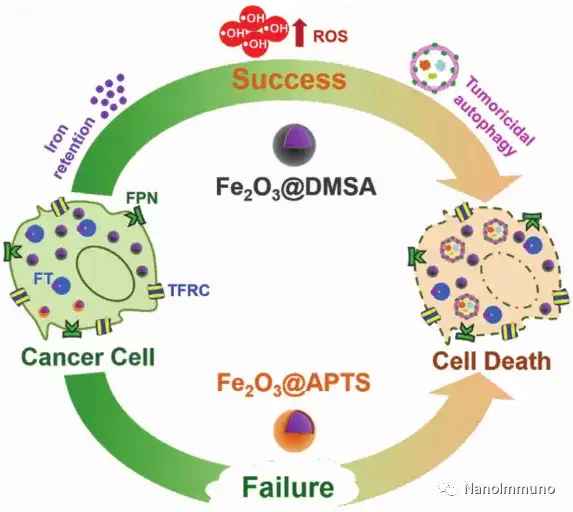
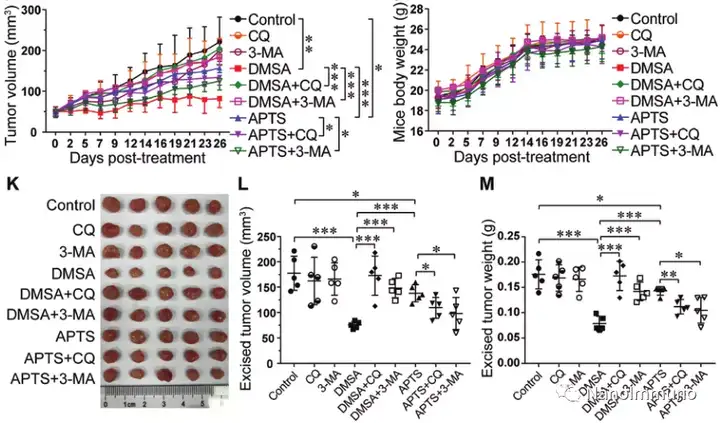
The combination therapy of nanoparticles and autophagy inhibitors, such as chloroquine (CQ) and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), has been extensively studied in tumor treatment. However, the toxicity and low selectivity of autophagy inhibitors seriously hinder the application of combination therapy. Liu Peifeng, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, designed and identified a carboxyl functional iron oxide nanoparticle (Fe2O3@DMSA), which has a significant anti-tumor autophagy effect without adding CQ or HCQ. Further studies have shown that the effective inhibitory effect of Fe2O3@DMSA on the growth of liver cancer is triggered by inhibiting the fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes to enhance anti-tumor autophagy. This fusion is induced by intracellular iron retention. Induced by continuous production of reactive oxygen species. In two tumor-bearing mouse models of liver cancer, Fe2O3@DMSA alone can effectively inhibit tumor growth without obvious side effects.
18915694570
Previous: Applied Surface Scienc


