Trends in Chemistry: MXenes as an energy storage electrode


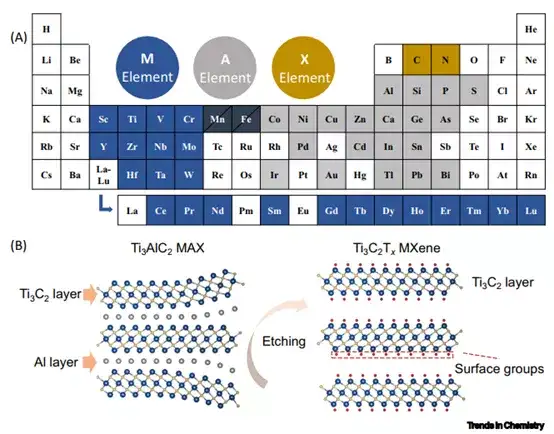
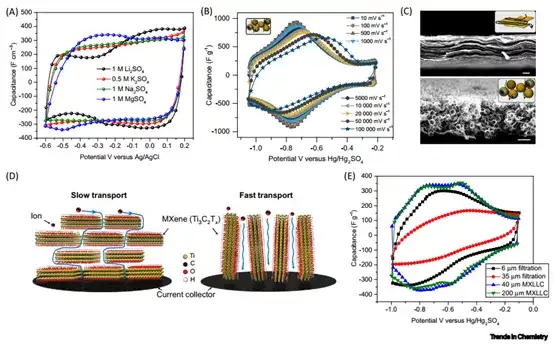
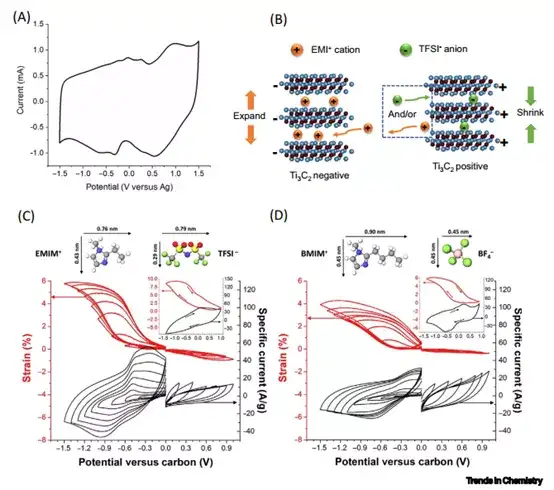
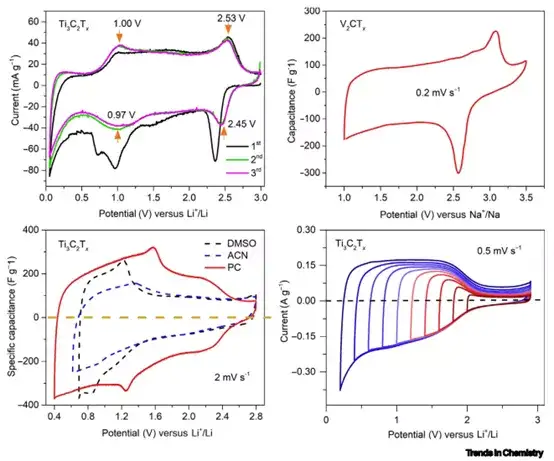

In the future, researchers need to conduct in-depth research in the following aspects: 1) Taking the Lewis acid molten salt method as an example, explore environmentally friendly, safe, and efficient batch-capable sound field methods to expand the MAX phase precursor and the surface composition of MXenes The controllable equipment. 2) In all MXene research work, about 70% of the research focused on the first discovery of MXene, which is Ti3C2Tx. Although the preparation process of other types of MXenes is more complicated, we need to conduct in-depth exploration from both theoretical and experimental aspects. 3) Although MXene electrodes can achieve higher capacity in aqueous electrolytes, considering the wider voltage window, the performance of MXene in non-aqueous electrolytes should be studied more deeply. Optimal regulation of the composition and nature of MXene surface functional groups, as well as the control between layers, are crucial to the improvement of performance. 4) For electrochemical capacitors and high-power batteries that need to meet high power and high energy density at the same time, design 3D porous, vertical arrangement or other structure of MXene electrodes to improve without sacrificing too much volumetric energy density. The ion transmission path in the electrode will become the key development direction in the next few years.
Literature link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trechm.2020.04.010
This information is sourced from the Internet for academic exchanges. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately
18915694570
Previous: Professor Braeckmans,


