Yury Gogotsi Team: Ten Years of Progress in MXene Synthesis and Development

one. Article overview
Since its discovery in 2011, the number of two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) has steadily increased. There are currently more than 40 manganese components. The final number is much larger, and over time, they may develop into the largest known family of two-dimensional materials. The unique characteristics of MXenes, such as the conductivity of similar metals up to ≈20 000 S·cm−1, make them very useful in many applications, including energy storage, optoelectronics, biomedicine, communications, and the environment. The number of MXene papers and patents has grown rapidly. The first generation of MXene was synthesized by selective etching of the MAX phase metal layer, layered transition metal carbides and carbides using hydrofluoric acid. Since then, a variety of synthesis methods have been developed, including selective etching in mixtures of fluoride salts and various acids, non-aqueous etchants, halogens and molten salts, allowing the synthesis of new dienes and better control of their Surface chemistry. The article briefly introduces the historical overview of the first 10 years of MXene research, and prospects its synthesis and future development. In fact, their production is easy to expand in an aquatic environment, and their high production augurs well for their commercialization.
Two, graphic guide
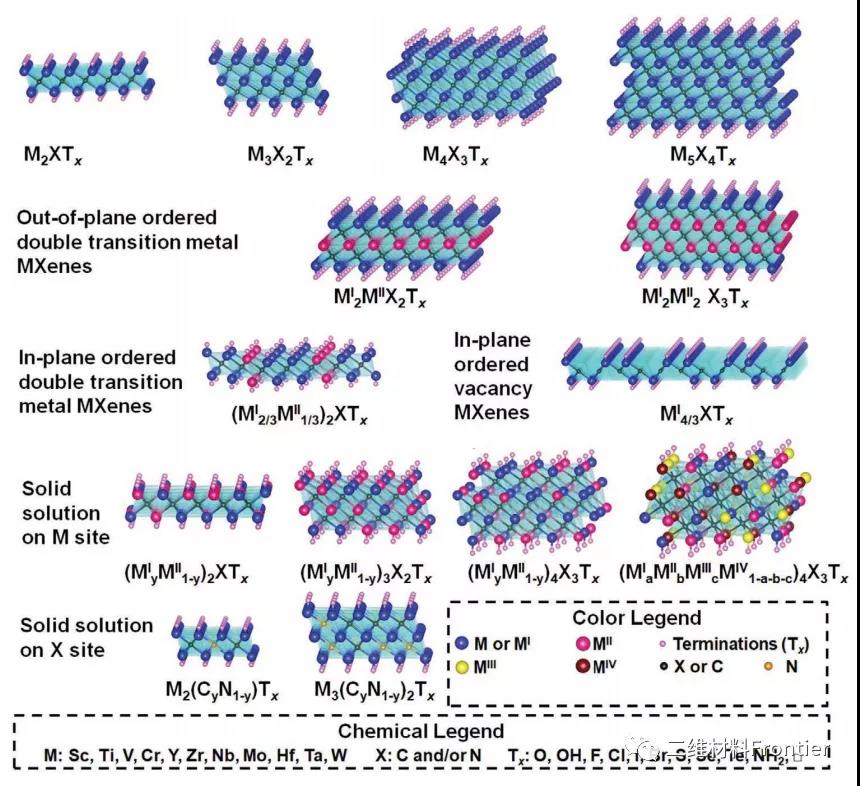
Figure 1. Typical MXene structure and composition.
MXenes has a formula of Mn+1XnTx, where M is an early transition metal, X is C or N, and Tx represents the surface end. The value of n can vary from 1 to 4. The M site can be occupied by one, two or more transition metal atoms to form a solid solution or ordered structure. Ordered double transition metal MXenes exist as in-plane ordered structures (i-MXenes), for example, (Mo2/3Y1/3)2CTx, in-plane vacancy structures, such as Mo2/3CTx and out-of-plane ordered structures (o- MXenes), in which one or two layers of MII transition metal are sandwiched between MI transition metal layers, such as Cr2TiC2Tx or Mo2Ti2C3Tx.
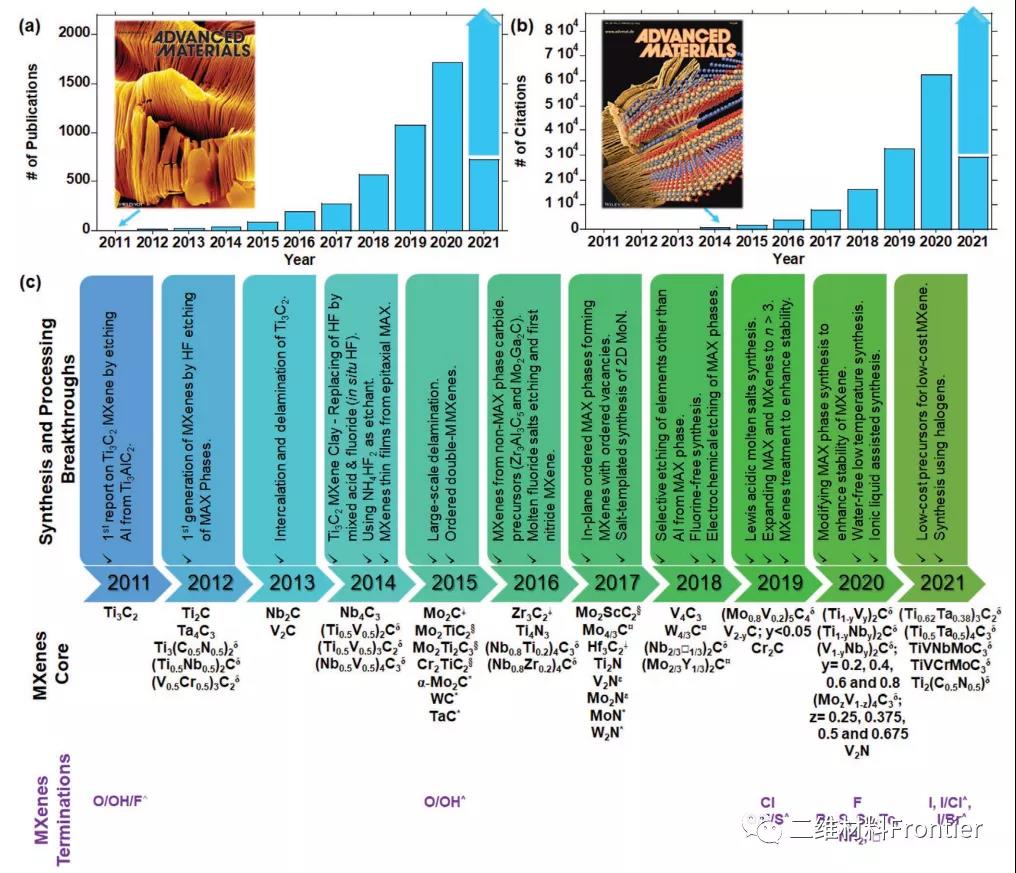
Figure 2. Time sequence introduction of research progress in the field of MXenes.
The illustration in (a) is the number of articles found by Ti3C2Tx MXene, and the illustration in (b) is the number of the first comprehensive review in this field. (c) A list of the major synthesis and processing breakthroughs in the first 10 years of MXenes research, the new core components of MXene discovered during the decade (for simplicity, the chemical formula omits surface termination abbreviated to Tx), and the progress in surface termination control. Solid solution δMXene; non-MAX phase precursor MXene; out-of-plane ordered double transition metal MXene; in-plane ordered double transition metal MAX phase analog ¤MXene; *bottom-up two-dimensional carbide and nitrogen Compound; Epsilon nitride MXene produced by the post-processing of carbide MXene synthesis; □ Vacancy and ^ mixed terminal.
3. Full text summary
The unique characteristics of MXenes, their good performance in a wide range of applications, and their scalable synthesis make them attractive for research and technological development, as can be clearly seen from the large number of papers and patents that have appeared in the past few years. The composition of MXenes has countless possible compositions, and the number of these materials will continue to grow, and MXenes may become the largest family of two-dimensional materials. Replacing carbon with nitrogen changes the electronic structure of MXene, thereby changing its properties. So far, attempts to produce MXenes with X=B (MBenes) have limited results. Other calculated and predicted two-dimensional carbides, nitrides and borides are still waiting to be synthesized, and efforts should be made to synthesize these materials. The continuous development of different synthesis methods is of great significance for the realization of new MXene compositions and the production of controlled uniform surface terminations.
This information is sourced from the Internet for academic exchanges only. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately.
18915694570
Previous: Review of Queen’s Univ


