Peptides
The company provides the following peptide services
On February 3, 2021, Nature Reviews Drug Discovery published a review article by scientists from the University of Queensland and the University of Wollongong in Australia on the trend of peptide drug development.

In 1922, Canadian scientists Banting, Berclyde and others successfully isolated insulin, turning diabetes from a disease in which no cure can be taken but starvation therapy to a controllable chronic disease. The discovery of insulin also witnessed the beginning of peptide drugs. Subsequently, a number of hormone peptide drugs have entered the clinic one after another. In 1982, Genentech/Lillys recombinant insulin was approved for the market, and genetic engineering drugs gave more design space for the secondary research and development of peptide drugs.
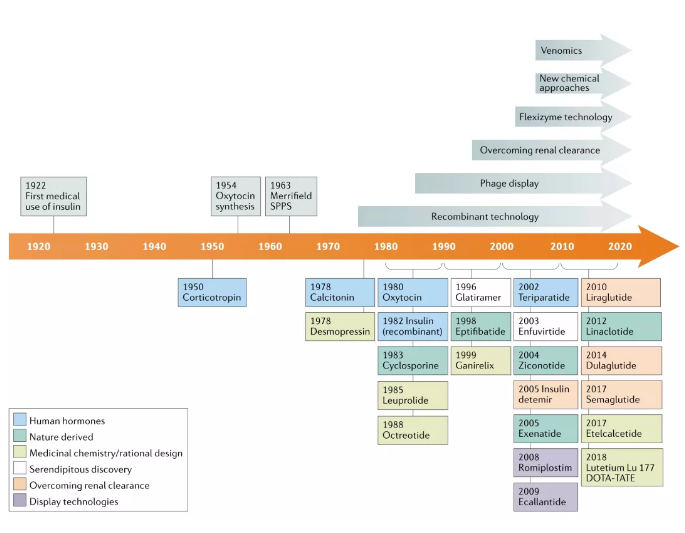
Since the 1960s, more than 80 peptide drugs have entered the clinic. In addition to insulin, ACTH, GLP-1, etc., natural products have become another important source of peptide drugs.
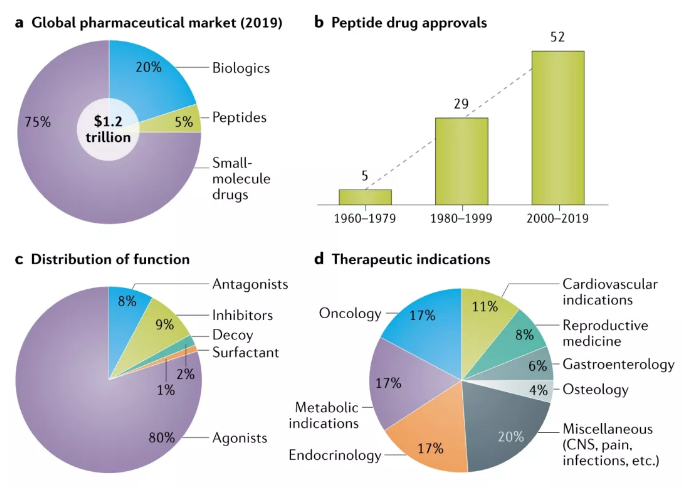
Insulin is still the largest peptide drug in the market, but it has entered a decline phase. GLP-1 will rapidly replace insulin as the most important hypoglycemic drug in the next few years, and will continue to make breakthroughs in obesity, cardiovascular, renal protection, NASH and other indications. The sales of dulaglutide in 2020 are US$5.068 billion, semaglutide is US$3.5 billion, and liraglutide is US$3.1 billion.
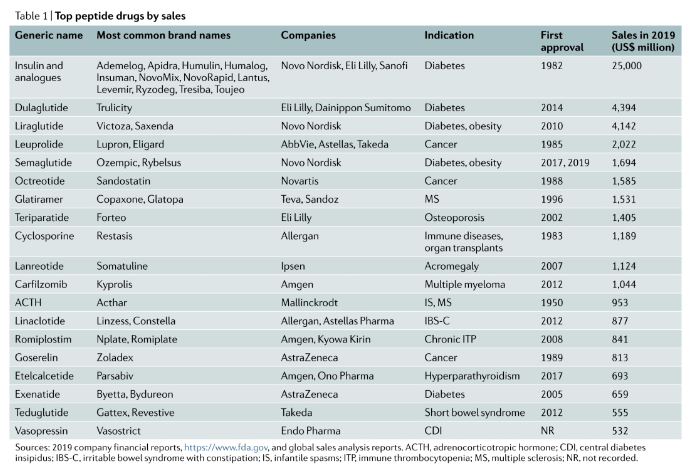
Peptide hormones are widely used clinically, but natural peptides are often not suitable for direct use as clinical drugs, especially in terms of pharmacokinetics. It is often necessary to improve their pharmacokinetic characteristics to facilitate administration and better simulate physiological secretion of hormone release curve. The following figure lists the optimization of somatostatin and insulin. Nordnorths new generation of weekly insulin Icodec has also entered Phase III clinical trials. Through fatty acid linkage modification and reduction of insulin receptor affinity, the half-life and dosing cycle are greatly extended.
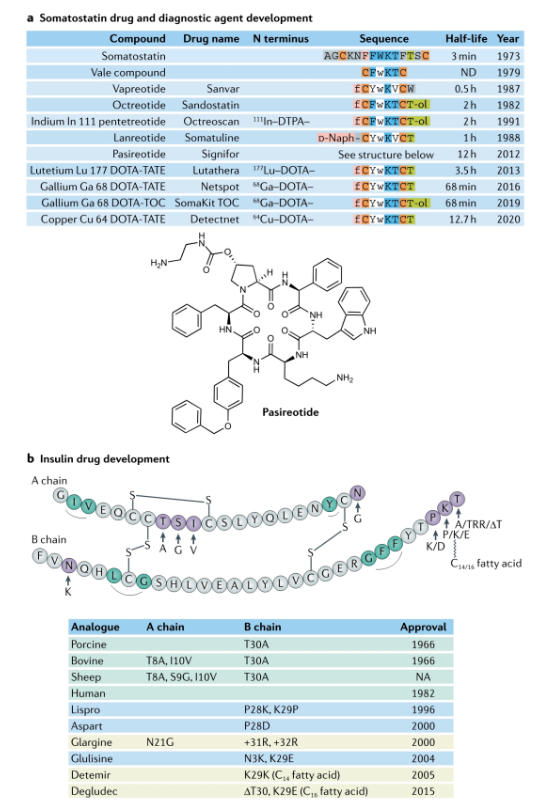
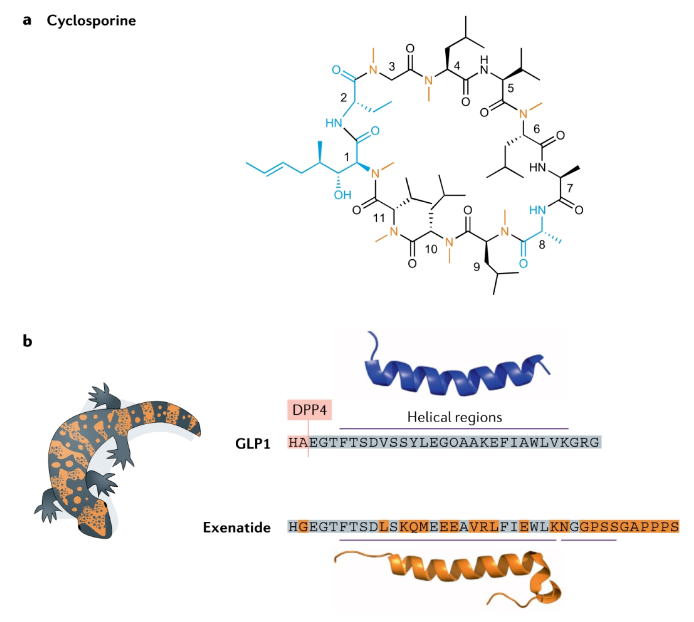
Natural products are an important source of peptide drugs, such as cyclosporine discovered in the 1960s and 1970s. This is an 11 amino acid cyclic peptide isolated from the fungus Trichoderma porous, and contains a rare D-amino acid. Cyclosporine can bind to cyclophilin to inhibit calcineurin and play an immunosuppressive effect. Cyclosporine is clinically used in the treatment of a variety of autoimmune diseases. Aurinias vorocycline was just approved last month for the treatment of lupus nephritis, which is an improved version of cyclosporine. Exenatide is the first GLP-1 to be a drug. Due to the short half-life of natural GLP-1, it cannot be made into a drug. Exenatide is only 53% homologous to human GLP-1 and cannot be used by human DPP-IV. Cut, the half-life can reach 3-5 hours. However, with the development of human GLP-1 analogs, Exenatide has declined.
Based on the development of natural products, especially toxicomics (Venomics), it has become an important direction for the research and development of peptide drugs.
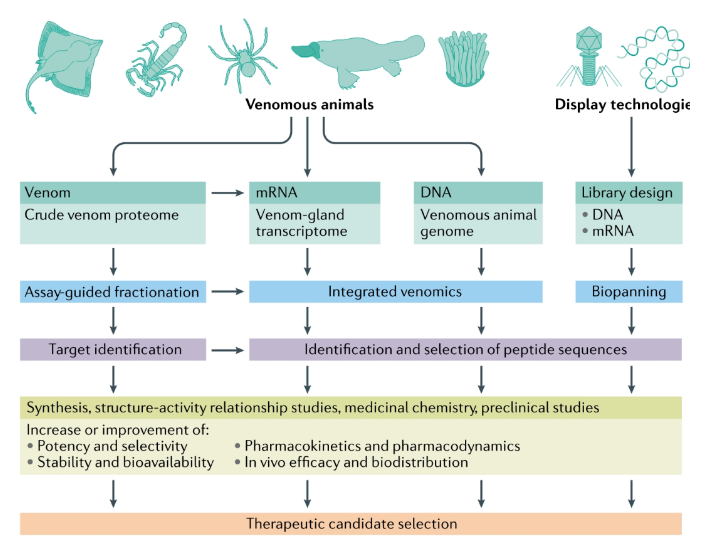
Ion channels are the targets of many animal toxin peptides.
to sum up
The combination of medicinal chemistry and peptide drugs can greatly expand the application space of peptide drugs. The fusion protein strategy can also play a specific role such as extending the half-life. In recent years, the discovery, modification and optimization of peptide drugs, and the route of administration have made considerable progress, and more and more new breakthroughs will be made in the future.
18915694570
Previous: Nature communications
Next: Biological microsphere


