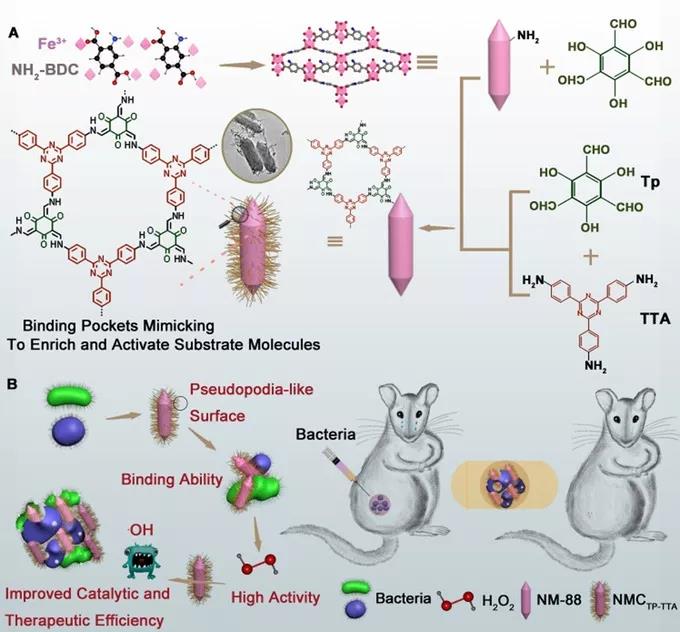
Bionic construction of pseudopodia like surface MOF@COF Application of nanoenzyme in inhibiting bacteria
Introduction
A large number of studies have reported that metal organic frameworks (MOFs) have the function of mimicking enzymes. However, due to their low enzyme like catalytic activity, their catalytic performance and therapeutic effect are not satisfactory. Based on this, researchers Qu Xiaogang and Ren Jinsong of Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry of Chinese Academy of Sciences published nature inspired construction of science on Angewandte Chemie International Edition in 2021 MOF@COF Nanozyme with active sites in tailored microenvironment and pseudopodia like surface for enhanced bacterial infection, In this study, we used natural inspiration to design and construct a platform with custom microenvironment active sites and pseudopod surface MOF@COF Nanoenzyme (nmctp-tta) can enhance the catalytic and therapeutic efficiency of nanoenzyme. Nmctp-tta was synthesized by sequential growth . First, nm-88 was prepared by solvothermal method and nm-88-cho was formed by Schiff base reaction. Then, nm-88-cho was constructed by covalently linking TP and TTA. Finally, nm-88-cho was linked to nm-88-cho to form nmctp-tta. The obtained nanoparticles form a specific microporous environment around the active sites, which can enrich and activate the substrate molecules through non covalent interaction. This kind of branched structure nanoenzyme can capture bacteria and produce ROS like the pseudopodia of neutrophils, which can effectively kill bacteria.
research contents
one MOF@COF Synthesis and characterization of a novel polymer
Nh2-mil-88b (FE) (nm-88) with peroxidase like activity was used as model nanoenzyme to form aldehyde functionalized nanoenzyme nm-88-cho by Schiff base reaction. Coftp-tt was constructed by covalent conjugation of TF with TP and TTA. Finally, coftp-tta and nm-88-cho were covalently linked by solvothermal method MOF@COF Nanoenzyme. SEM, EDS and FTIR showed that MOF@COF The successful preparation of nanoenzyme (Fig. 1, a, B, C, I); COF TP TTA, nm-88 and NMC TP TTA ζ Potential (Fig. 1D); The peroxidase like activities of NMC TP TTA and nm-88 under different pH conditions (Fig. 1f, g). The researchers observed that compared with nm-88, MOF@COF The peroxidase like activity of TMB was significantly increased, and only coftp TTA could not catalyze the oxidation of TMB. Therefore, MOF@COF The enhanced catalytic ability of coftp TTA may be attributed to its advantages in the composition and structure of coftp TTA, as well as providing active sites in the surrounding microenvironment to mimic the function of amino acid residues and activate the catalytic reaction with the substrate, thus enhancing the catalytic ability. It was observed by SEM and TEM MOF@COF It has pseudopodia shape and porous structure.
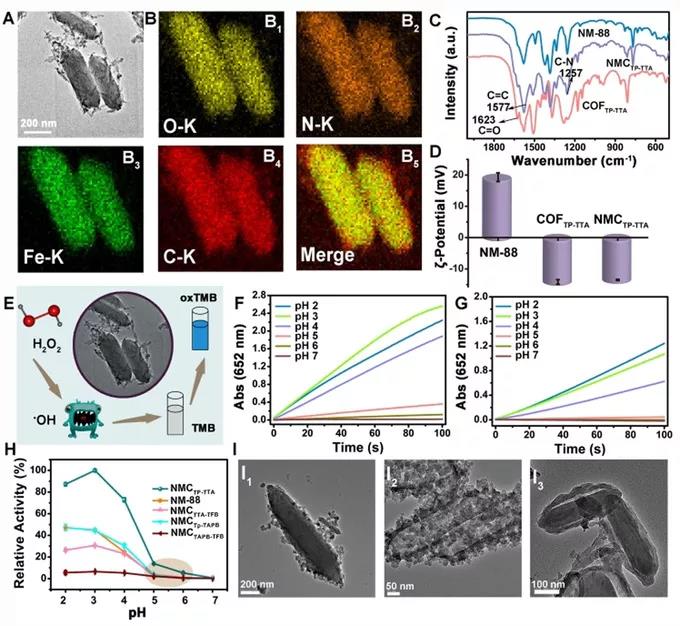
Fig. 1, a) TEM image of nmctp TTA; B) EDS image; C. D) FT-IR and IR spectra of coftp TTA, nm-88 and nmctp TTA ζ Potential; E) The peroxidase like activity of nmctp TTA was shown; F. G) the peroxidase like activities of nmctp TTA and nm-88 were determined by monitoring the absorption of TMB at 652 nm at pH 2 – 7. H) Their peroxidase like activities were qualitatively analyzed; 1) TEM images of nmctta-tfb, nmctp tapb and nmctapb-tfb.
two MOF@COF Interaction with bacteria
Based on the fact that neutrophils form pseudopodia to surround and capture bacteria, the researchers speculate that they have pseudopodia like morphology MOF@COF It can capture bacteria tightly and kill bacteria effectively by ROS produced in situ. Next, yes MOF@COF In this study, six different groups were set up to study their antibacterial activities against drug-resistant staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli MOF@COF H2O2 significantly inhibited the growth of both bacteria in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 2a, b). The results of plate counting and quantitative analysis showed that nm-88 alone almost did not inhibit the growth of bacteria, nmctp TTA alone showed a slight decrease, while nmctp TTA alone did not inhibit the growth of bacteria MOF@COF The combination with H2O2 was more effective than other groups in reducing bacterial survival rate (Fig. 2e). And SEM test results show that there are pseudopodia samples MOF@COF Tearing the bacterial cell wall tightly causes slight structural deformation, which may be due to MOF@COF Multivalent topological interactions with the bacterial cell wall of the bacterium (Fig. 2f). MOF@COF The enhanced antibacterial effect of combined with H2O2 is due to MOF@COF Enhanced binding to bacterial cell walls, and MOF@COF It can destroy pathogens more directly and effectively by producing in situ oh.
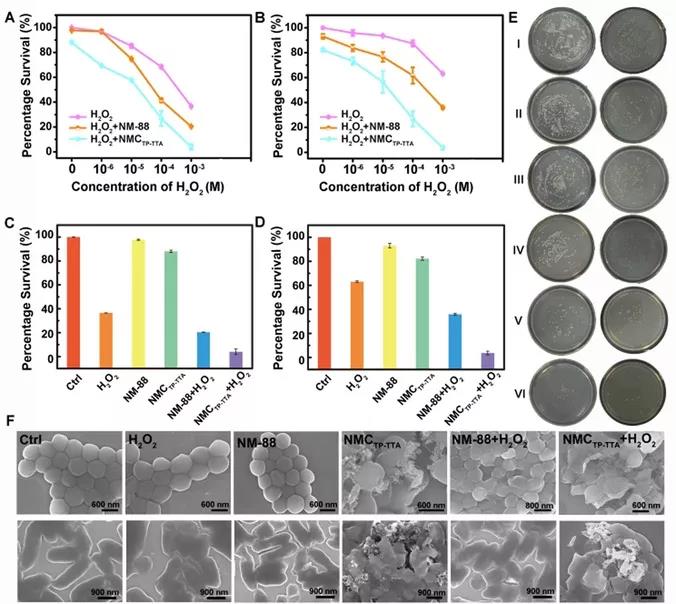
Figure 2. The survival rates of Staphylococcus aureus (a) and Escherichia coli (b) after CO incubation with H2O2 under different treatment conditions; The survival rates of Staphylococcus aureus (c) and Escherichia coli (d) after different treatments were compared; E) The colony pictures of Staphylococcus aureus (left) and Escherichia coli (right) under different treatments were as follows: (I) PBS, (II) H2O2, (III) nm-88, (IV) nmctp TTA, (V) nm-88 + H2O2, (VI) nmctp TTA + H2O2( F) SEM images of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.
three MOF@COF Promote wound healing
Next, further study MOF@COF In vivo application. The potential of eliminating bacteria in vivo was explored by using mouse wound infection model. The researchers constructed the wound model of Staphylococcus aureus infection and used different treatment methods. The results showed that mild inflammation and some collagen formation were found in nmctp TTA + H2O2 group, and the number of colonies in nmctp TTA + H2O2 group was the least (Fig. 3, C, d). After 5 days of treatment, nmctp TTA + H2O2 group showed the best wound healing effect and the smallest wound area (Fig. 3b). Therefore, it can be concluded that coftp TTA can enhance the catalytic and therapeutic properties of nm-88 nanoenzyme, and show a gratifying antibacterial effect.

Fig. 3, a) schematic diagram of treatment strategy for Staphylococcus aureus wound infection model; B) On day 1 and day 5, images of wound infection models were processed with different processing methods( C) Images of bacterial colonies isolated from wound tissue by different processing methods; D) After 5 days of treatment, the skin tissues obtained from mice were stained with H & E and collagen I immunohistochemistry (scale 50) μ m)。
summary
MOF@COF The metal node of MOF is used as the active center of nanoenzyme, and the subsequent growth of COF structure will produce multi-level nano cavities to form a suitable pore environment near the active site, which can enrich and activate the substrate molecules, and then enhance the inhibition of bacteria. In addition, the pseudopodia like surface of COFS enables the system to effectively capture bacteria, thus further enhancing the therapeutic efficiency of the nanoenzyme. In conclusion, this research can not only promote the development of new nano enzymes, but also broaden the biological application of MOF / COF based hybrid materials.
This information is from the Internet for academic exchange only. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately
18915694570
Previous: Shenzhen University Hu
Next: Nature communications


