Mate. Horiz. By Prof. Feng Wei and Prof. Wang Ling of Tianjin University: liquid metal composite liquid crystal polymer actuators for programmable software robots
Nature has always been a source of inspiration for human beings to imitate the biological softness, body compliance and important functions of various organisms. Recently, bionic soft robots based on responsive soft materials have attracted more and more attention. Compared with the traditional rigid robot, the soft robot has the unique advantages of structural deformability, human-computer interaction friendliness, high degree of freedom, environmental compliance and adaptability. Previous studies based on soft materials such as hydrogel, liquid crystal network (LCN) and shape memory polymer (SMP) have shown that LCN is considered to be one of the excellent candidates for the preparation of actuators driven by actuators due to its anisotropic, reversible and programmable shape and deformation characteristics. However, LCN based soft robot systems are usually limited by their inherent lack of thermal or electrical conductivity and mechanical incompatibility with functional nanomaterials. In addition, gallium based liquid metals (LMS) are also used to develop soft robots because of their excellent fluidity, high thermal conductivity and conductivity. However, their deformation and adaptive motion are mostly driven by electric field or chemical stimulation, and they often prevent surface oxidation in acidic aqueous solution environment, which greatly limits their functions and potential applications. Therefore, it is urgent to propose a soft matter engineering strategy to effectively combine liquid metals with functional polymers or nanomaterials and maintain their excellent intrinsic properties.
In view of this, Professor Feng Wei and Professor Wang Ling of Tianjin University, together with Academician Li Quan of Kent State University, proposed a universal strategy to integrate conductive liquid metal (LM) and shape morphing liquid crystal network (LCN) into multifunctional and programmable soft robots. The shape programmable lm-lcn actuator not only combines the reversible shape deformation characteristics of LCN and the excellent thermal / conductive properties of LM, but also realizes the electrothermal driving and near-infrared (NIR) driving. In order to verify the function of the soft robot, researchers have developed a self sustained soft oscillator and a soft crawler driven by near-infrared light (NIR), and skillfully combined the programmable soft robot with traditional shadow play art, showing the scenes of shadow play such as police waving traffic, Chang e running to the moon and poets looking up at lighthouses based on the light driven soft actuator. The strategy proposed in this work is expected to open up a new technical field for the research of advanced multifunctional soft materials. The related work was published in materials horizons, an international authoritative material journal, as a paper entitled stulus driven liquid metal and liquid crystal network actors for programmable soft robotics.
Reversible shape deformation of lm-lcn actuator under DC voltage or NIR light irradiation
The researchers designed and synthesized biomass nano bacterial cellulose through biological culture technology. Then, the eutectic gallium indium (egain) LM and miniature carboxylated gold nanorods (minignr-cooh) were ultrasonically treated in the aqueous suspension of biological nano cellulose, and a unique colloidal LM ink was ingeniously designed and manufactured. The introduction of minignr-cooh can not only stabilize LM nanoparticles, but also greatly enhance the photothermal properties of colloidal LM ink. A deformable lm-lcn actuator with LCN thickness of ~ 23 mm was fabricated by coating colloidal LM suspension on LCN film μ m. The thickness of LM coating is about 0.3 μ m)。 The lm-lcn actuator exhibits reversible shape deformation when applied with DC electric field or near-infrared light irradiation (as shown in Fig. 1), which is due to the decrease of liquid crystal ordering induced by electrothermal and photothermal, and the resulting planar orientation side shrinkage and vertical orientation side expansion of the film. The bending angle of lm-lcn actuator can be controlled by low DC voltage, and the bending angle can reach 34 in 3.0 seconds at 1.5 v °, The original shape was restored within 2 s after the voltage was removed. The photoresponse dynamics of lm-lcn actuator is closely related to the thickness of LCN film, the thickness of colloidal LM coating and the power density of near infrared radiation. Lm-lcn actuator can reach 118 nm in 2.5 seconds under NIR light (808 nm, 0.3 Wcm-2) ° And this shape deformation has excellent cyclicity.
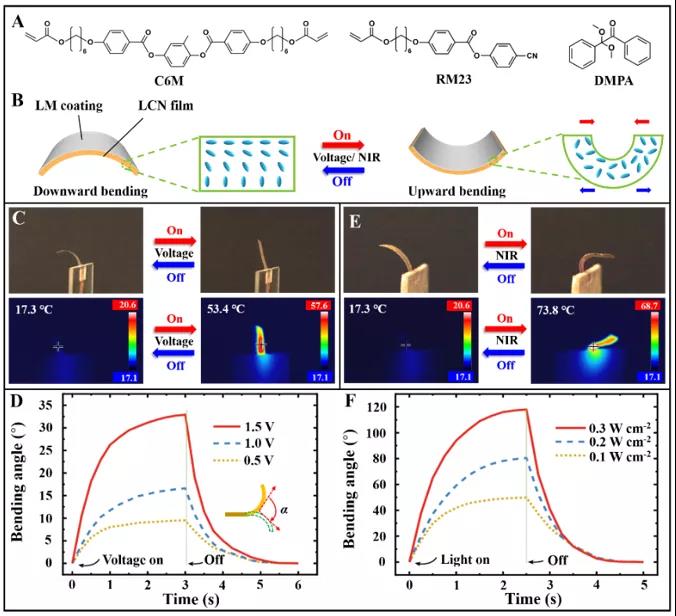
Fig. 1 reversible shape deformation of lm-lcn actuator after DC voltage or NIR light irradiation
NIR light driven shape programmable lm-lcn actuator
The shape deformation and time programming function of lm-lcn actuator driven by NIR are attributed to the excellent photothermal conversion efficiency of embedded minignr-cooh and the selective coating characteristics of colloidal LM ink. The programmable deformation ability of lm-lcn brake can be realized by coating colloidal LM ink on the selected area on the plane side of LCN film arranged obliquely (as shown in Fig. 2). When the nanostructured colloidal LM coating is only deposited on one side, middle and both ends of LCN film, the reversible S-shaped, M-shaped and W-shaped driving can be obtained under NIR light irradiation, respectively. Inspired by the oscillation phenomena in nature, such as dragonfly wings, researchers developed a NIR photo fuel lm-lcn self-sustaining soft oscillator with a frequency of about 8.0 Hz by depositing a colloidal LM coating on one side of the LCN film, based on the self shadowing mechanism caused by photothermal and optical bending deformation. The researchers further mimic the inchworm crawling in nature. In the light on / off cycle, they show a light driven soft robot crawler, which is made of the center pattern lm-lcn translocated on the ratchet substrate. Under the irradiation of NIR, lm-lcn actuator moves forward because of the different friction between the front and back edges when LCN surface bends downward (F1 > F2). After closing NIR, the LCN strip elasticity recovers, and the leading edge bears large friction (F4 > F3) to make the rear track move forward. In addition, it is found that the crawling speed of lm-lcn actuator is closely related to the intensity of infrared light. When the intensity of 808 nm infrared light is 0.1, 0.2 and 0.3 Wcm-2, the average crawling speed of lm-lcn actuator is 1.17, 1.51 and 1.75 MMS-1, respectively.
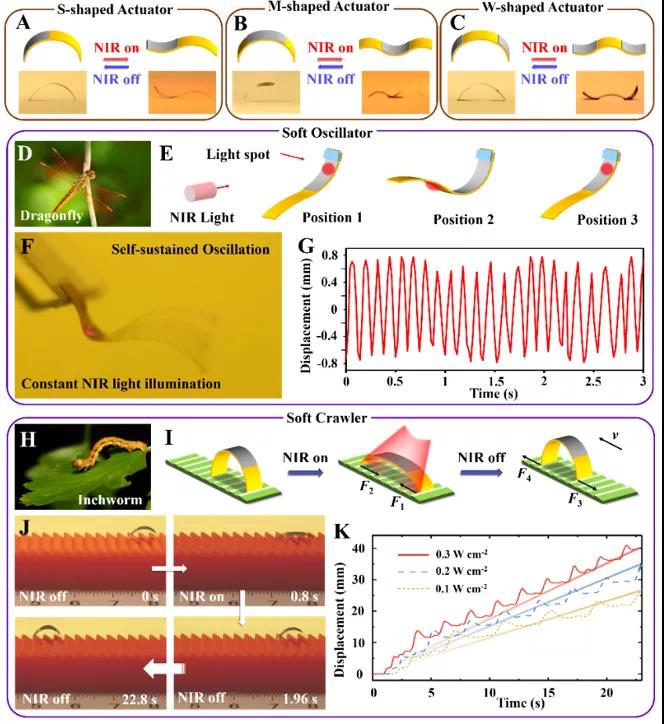
Figure 2 programmable lm-lcn soft actuator with NIR light driven shape
By assembling lm-smp with shape memory behavior and lm-lcn actuator with deformable conductive shape, the researchers also integrated a light controlled programmable robot shadow play, in which all movements are projected onto the screen observed by the audience (as shown in Figure 3). The police in charge of traffic is made of reversible lm-lcn (hand) and irreversible lm-smp (body) actuators. At the beginning, the shadows of the police and the car are not visible to the screen in the horizontal state. When the NIR light irradiates, the irreversible deformation of lm-smp hinge induced by light and heat causes the shadows of the car and the police to appear on the screen successively. Lm-lcn actuator is used as elbow joint in one hand of police, which can show reversible hand waving gesture through circular NIR light irradiation. The second robot shadow play, inspired by the legend of Chang e flying to the moon in Chinese legend, shows a jade rabbit walking towards a beauty. Under NIR radiation, the irreversible deformation of lm-smp hinge on Meiren s foot caused her appearance. The light driven Yutu to beauty is triggered by lm-lcn actuator shifting on the ratchet ladder under cyclic near infrared radiation. The last shadow play, based on the conductivity of lm-lcn and lm-smp soft actuators and colloidal LM coating, shows a poet looking up at a shining lighthouse. The appearance of human shadow is also based on the near-infrared radiation of lm-smp hinge, while the red LED on the top of the lighthouse switches reversibly based on the bending deformation of conductive lm-lcn film driven by NIR light, making the circuit connected or disconnected.
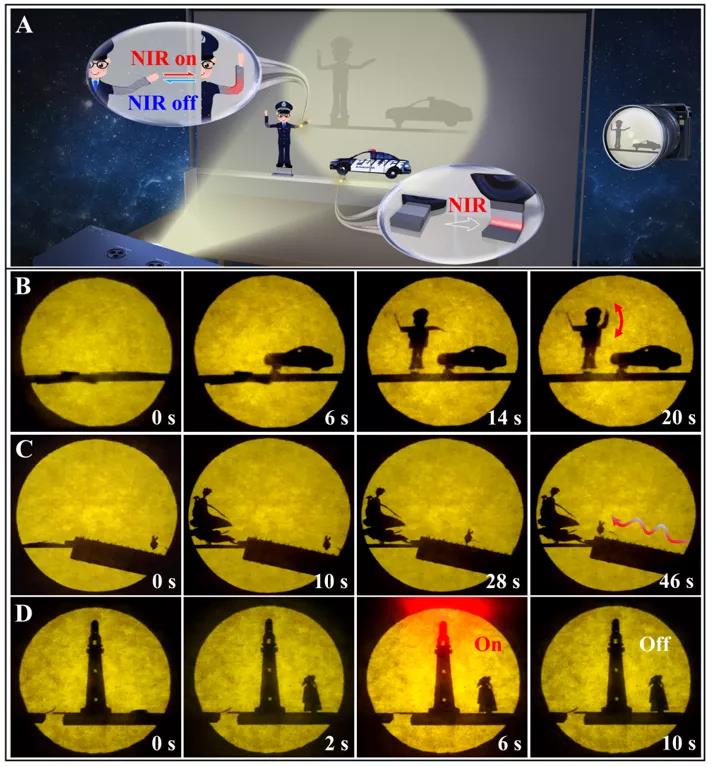
Fig. 3 shadow show of a programmable soft robot combined lm-lcn and lm-smp under NIR light
summary
Based on the reversible shape deformation characteristics of LCN and the excellent conductivity of LM, a shape programmable lm-lcn soft actuator driven by electro thermal and photothermal was developed. By selectively coating colloidal LM ink on LCN thin films with unfolding molecular orientation, a NIR light driven shape programmable lm-lcn soft actuator with various shapes was developed. In addition, by combining lm-lcn and lm-smp, the researchers applied the programmable soft robot to the traditional shadow play art, showing the scenes of shadow play such as police directing traffic, Chang e flying to the moon and poets looking up at lighthouses based on light driven soft actuators. This work shows a more general strategy, which can effectively integrate the conductivity of LM and the shape deformation characteristics of LCN or functional polymers, and maintain their excellent intrinsic characteristics, providing new power for the development of cordless soft robots or machines with bionic intelligence, integrated multi-functional flexible electronic devices, human-computer interaction and other advanced biomedical technologies.
This information is from the Internet for academic exchange only. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately
18915694570
Previous: CEJ effectively organi


